“From a macro perspective, it is better to repair than to demolish and rebuild. This is a fundamental idea in terms of both cost and the environment”
Materiality analysis
Reducing emissions is a top priority for Ocab’s ability to meet the science-based targets it has adopted. In addition, several of our stakeholders have set their own science-based targets that require us to work together to reduce emissions.
We see economic advantages in reducing emissions and creating a more sustainable business. Damage prevention is a high priority for customers because damage represents a loss in terms of costs and resources.
For Ocab, we see opportunities in offering more preventive services as we have good knowledge about where and when damage occurs. Since the company's inception, we have managed damage with the aim of saving value and thus minimising waste.
At Ocab, we see business potential in moving towards a more circular economy focused on resource efficiency, which means we constantly develop our business model to offer resource-efficient methods through restoration and dehumidification.
For Ocab and for our partners, transparency and business ethics are high priorities. At Ocab, we strive to be a good business partner and therefore have clear guidelines designed to minimise the risk of unethical incidents that could damage our brand.
Materiality analysis process
The materiality analysis is carried out in accordance with GRI with inspiration from CSRD and the double materiality analysis method. The material topics have been approved by the Group CEO and Board of Directors.
The process for determining our material topics involved identifying the actual and potential negative and positive impacts that Ocab has on the environment, people, the economy and human rights.
The impacts were then assessed and prioritised. Insights from customers, suppliers, investors and employees were taken into account in the preparation of the materiality analysis and identification of the material topics.
The tools for identifying material topics are our risk analysis, our stakeholder and business environment analysis and the link to the global goals we have identified as material to our business. Prioritisation was based on the impact of each material topic on our business, the risk value of the topic and the potential for business and societal development.
Material topics
Our material topics have been updated from 2022, due to an expanded stakeholder dialogue. List of material topics:
Governance
Economic performance
Procurement practices (new for 2023)
Anti-corruption (new for 2023)
Environment
Energy
Emissions
Waste
Supplier environmental assessment (new for 2023)
Social
Employment
Occupational health and safety
Training and education
Diversity and equal opportunity
Non-discrimination
Supplier social assessment (new for 2023)
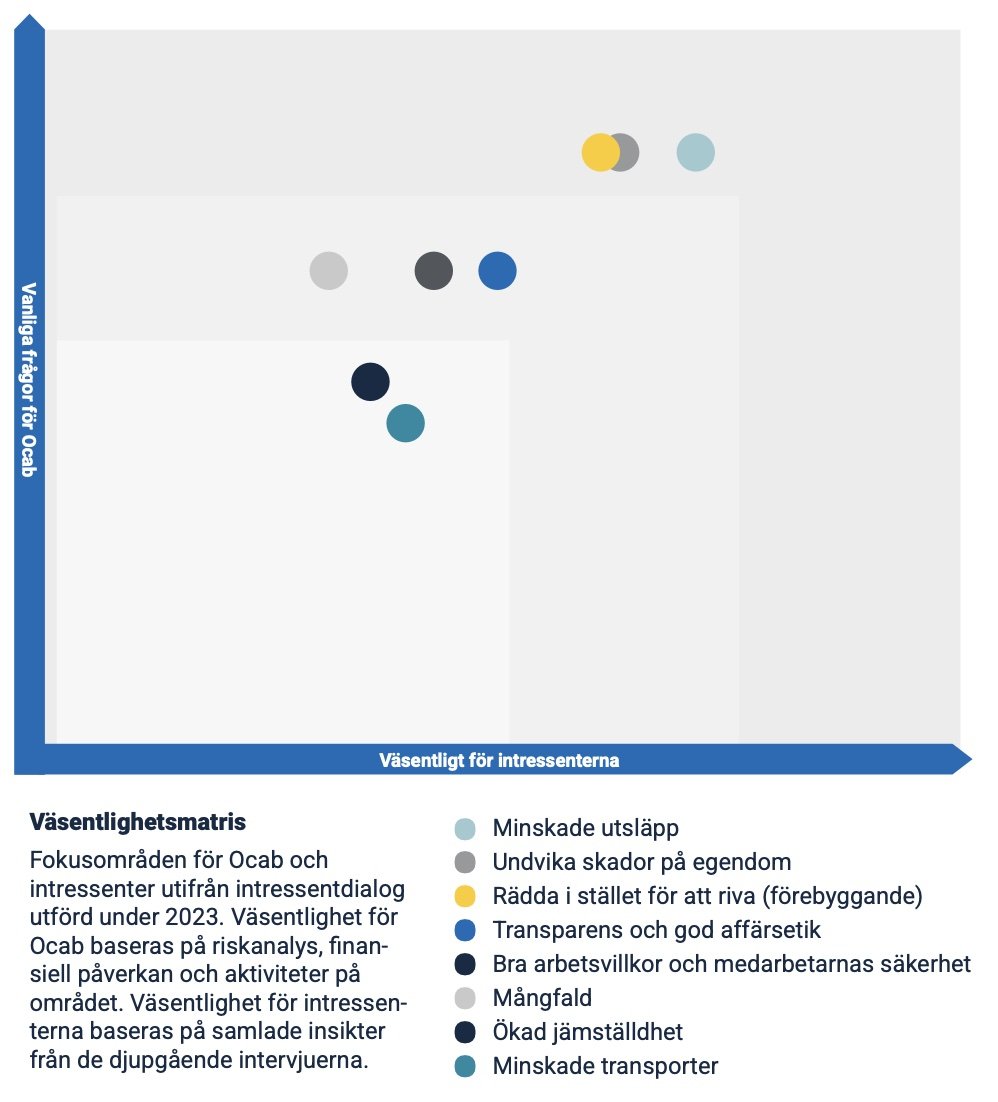
Materiality matrix
Focus areas for Ocab and stakeholders based on stakeholder dialogue conducted in 2023. Materiality for Ocab is based on risk analysis, financial impact and activities in the area. Materiality for stakeholders is based on the insights gathered from the in-depth interviews.
An open dialogue with our stakeholders
We see open dialogue with our stakeholders as a prerequisite for sustainable development. Our goal is to move the industry forward together and create a more circular economy in which we conserve resources and reduce emissions.
Read more about our strategy